Essential Tips for Understanding Overflow Valve Block Functionality?
In the world of hydraulic systems, the role of the Overflow Valve Block is crucial. These components ensure system efficiency and protect equipment from damage. A report from the Hydraulic Institute states that improper function of an overflow valve can lead to system failures, costing companies significant downtime.
Understanding the Overflow Valve Block is key to maintaining optimal performance. Many systems rely on these valves to regulate pressure. According to industry specialists, about 30% of hydraulic failures stem from valve issues. This statistic emphasizes the importance of regular maintenance and understanding valve functionality.
Operators must be aware of common pitfalls. Misinterpretation of overflow settings can lead to excessive pressure, risking equipment and safety. An effective strategy is to consult reliable manuals and industry reports. Learning from these resources can prevent costly mistakes and enhance system reliability.
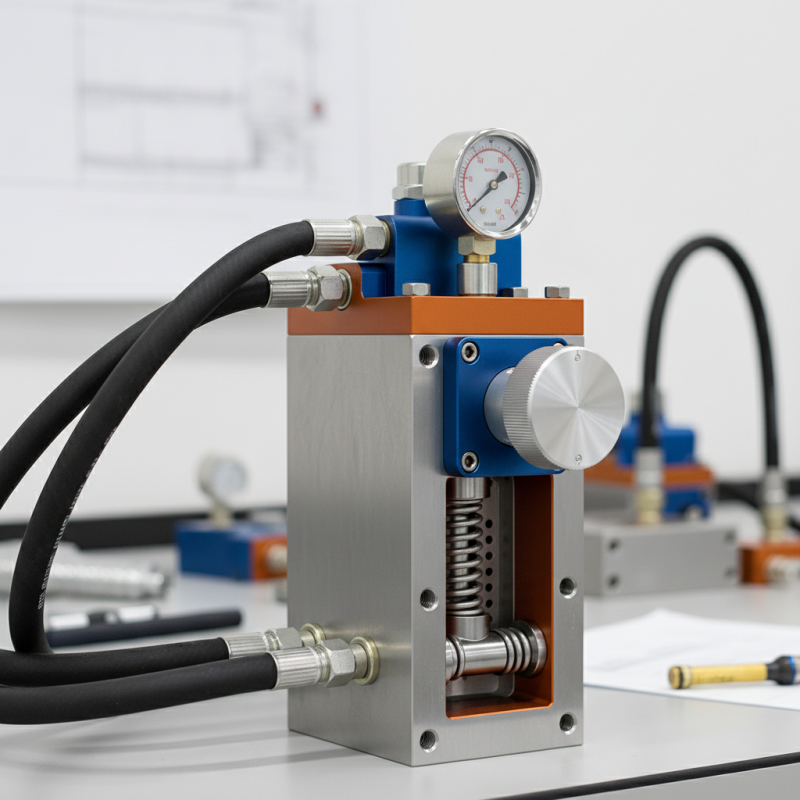
What is an Overflow Valve Block and Its Purpose?
An overflow valve block is a crucial component in hydraulic systems. It serves to regulate pressure and prevent damage. When the pressure exceeds a preset limit, the overflow valve opens. This action diverts excess fluid. As a result, it protects various system components.
The primary purpose of an overflow valve block is safety. Without it, a sudden surge in pressure could cause catastrophic failures. In maintaining optimal performance, these valves can help extend the lifespan of hydraulic equipment. They are often found in machinery, vehicles, and industrial systems. A properly functioning overflow valve block ensures that operations run smoothly.
Understanding its function can be complex. Over time, valves may wear out or become obstructed. This can lead to inefficiency or failure. Regular maintenance is essential. Operators should check for signs of damage or leaks. Ignoring these details can result in significant problems down the road.
Key Components of Overflow Valve Block Functionality
The overflow valve block plays a critical role in pressure regulation. It consists of several key components: the valve body, spring, and actuator. Each part must work together seamlessly. The valve body houses the internal mechanisms. It needs to be durable yet sensitive. If not, it may fail under pressure.
The spring generates force to open and close the valve. Different springs provide varying pressure thresholds. Choosing the right spring is essential for performance. An incorrect spring can lead to leaks or pressure spikes. The actuator responds to pressure changes. It is vital for timely adjustments to fluid flow.
Monitoring these components is crucial. Wear and tear can impact functionality. Regular checks prevent unexpected breakdowns. A worn spring may not respond instantly. In such cases, system efficiency decreases. Recognizing these imperfections can lead to better maintenance practices. This proactive approach enhances overall reliability. Understanding these functions helps in troubleshooting and optimization.
How Overflow Valve Blocks Regulate Pressure in Systems
Overflow valve blocks play a crucial role in regulating pressure within hydraulic systems. These components sense excessive pressure levels and activate to protect essential parts. When pressure exceeds a set limit, the valve opens. This action allows fluid to escape, preventing damage to system components.
The functionality of overflow valve blocks can be complex. Many factors influence their performance. For example, temperature and fluid viscosity play significant roles in how well these valves operate. If fluids are too thick, the valve might not respond quickly. This delay could lead to severe system malfunction. Understanding and addressing these variables is vital for reliable operation.
Installation and maintenance of overflow valves also require attention. Misalignment during installation can lead to leaks. Regular checks are necessary to ensure these valves work properly. Over time, wear and tear can affect their functionality. A small oversight in maintenance might compromise the entire hydraulic system. Users must be vigilant to maintain optimal performance.
Essential Tips for Understanding Overflow Valve Block Functionality
This chart demonstrates the performance metrics of overflow valve blocks, illustrating the relationship between flow rate, pressure setting, and response time. Understanding these aspects is crucial for optimizing system performance and reliability.
Common Applications of Overflow Valve Blocks in Industry
In many industrial settings, overflow valve blocks play a crucial role. They help manage fluid pressure and prevent system failures. Common applications include hydraulic systems and pneumatic controls. These blocks maintain safe operating conditions by routing excess fluid away from sensitive components.
Tip 1: Regularly inspect your overflow valve block for any signs of wear. Small leaks can lead to significant issues over time. Maintenance is vital for performance.
In chemical processing, overflow valve blocks protect equipment from pressure spikes. They prevent damage to pumps and pipes. Improper calibration could lead to catastrophic results. Understanding how they operate is essential for reliability.
Tip 2: Make sure you understand pressure settings. Each application might require different pressure thresholds. Adjusting them incorrectly can lead to operational failures.
Overflow valve blocks are essential, yet often overlooked. They are not a "set it and forget it" component. Regular checks and understanding their functionality can avert serious problems down the line.
Maintenance Tips for Ensuring Proper Functionality of Overflow Valves
Proper maintenance of overflow valves is crucial to their functionality. Regular inspections can prevent unexpected failures. According to a report by the International Society of Automation (ISA), nearly 30% of valve malfunctions arise from poor maintenance practices. Over time, dirt, debris, and corrosion can accumulate, leading to blockages. These blockages can cause improper valve operation, resulting in system leaks or pressure issues.
Routine cleaning is vital. It is recommended to clean overflow valves at least every six months. This helps to ensure that they remain operational. Personnel should examine seals and fittings regularly. Poor seal integrity can lead to leakage, which reduces system efficiency. Inadequate sealing can sometimes go unnoticed until a significant issue arises. Regular training sessions for maintenance staff can also enhance the knowledge around potential problems.
Monitoring system pressure is essential. Fluctuations may indicate an overflow valve issue. A consistent drop in pressure could point to leakage or blockages. Industry studies show that 25% of pressure problems are linked to malfunctioning valves. Therefore, understanding these signs can prevent larger system failures. Addressing these maintenance tips can enhance the longevity and reliability of overflow valves in any system.
Essential Tips for Understanding Overflow Valve Block Functionality
| Tip | Description | Maintenance Frequency | Importance Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Inspections | Check for leaks, corrosion, and damage to the valve casing. | Monthly | High |
| Clean the Valve | Remove dirt and debris to prevent clogging and ensure proper operation. | Quarterly | Medium |
| Test Valve Operation | Regularly check the operation of the overflow valve to ensure it opens and closes correctly. | Bi-Annually | High |
| Replace Seals | Check and replace seals to prevent leaks and maintain performance. | Annually | Medium |
| Calibrate Pressure Settings | Ensure optimal pressure settings for efficiency and safety. | Annually | High |
